

UX
User
eXperience
UX (User eXperience) deals with the global experience a user has when interacting with a software, application or a website. Although UX was originally meant to apply to any product or service, it is now primarily used in conjunction with digital products or services.
UX
UX encompasses all aspects of the end-user's interaction with the company, its services, and its products. UX is a lifestyle philosophy that isn’t limited to one particular need. Instead, it applies to all needs. In an ideal world, everything would be optimized to provide a high quality user experience. (Donald Norman)
History of UX design
The industrial design origin. Designers influenced with design for people: Henry Dreyfuss (Polaroid SX-70 Land camera (1972) , Design for Behavior: Dieter Rams and "less is more" (Braun T 1000, 1963)
In 1993 Don Norman (Cognitive psychologist and designer) coined the term “user experience” for his group at Apple Computer. Norman work on the Apple User Interface using the desktop methaphore for graphical user interface, (including windows, icons, and the cursor) of modern computers
In 2007, Steve Jobs introduced the first iPhone, which forever changed the digital world. The tactille touchscreen allowed people to do all the things we can't imagine our modern life without:
User
Research
Interaction
Design
Usability
Visual
Design
Branding
Content
UX
Writing
User Experience
UX Umbrella
Know as User Interface Design (UI), this specialization creates meaning in elements & interactivity in the screen through the use of fonts, colors, images, and space.
Visual Design
It's the systematic study of target users, requirements and insights to design processes. UX researchers methods: etnography, empathy, user stories, user journey, evaluations issues (A/B testing, questionnaires, surveys)
User Reseach
IxD is all about efficient interactions with interfaces. These designers may spend their time predicting user behavior, creating static mockups, and crafting product prototypes
Interaction Design
Usability is a measure of how well a specific user in a specific context can use a product/design to achieve a defined goal effectively, and efficiently and satisfactorily. Focus on: Engagement, Error Tolerance, Ease of Learning
Usability
It engages a dialogue between the product and the user, to create a fluent and useful experience, it is writing for the user through words, UX Writers make things more simple, so that users don’t have to effort a lot when they use a digital product.
UX Writing
This role highlights the business needs and goals for the product’s content. Strategists focus on the aspects of the brand from the perspective of a user, where consistency of tone, voice, and visual branding is key
Content
Why is UX relevant?
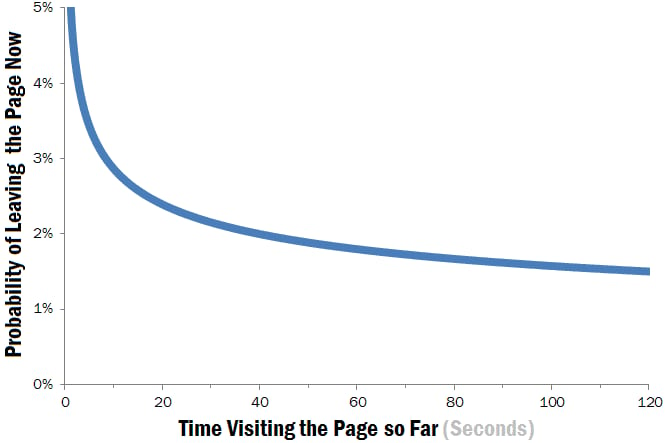
15 second rule
Time to leave a website?
How long do users stay on your website? Generally less than 15 seconds. That's the average time spent on a website and that's exactly how long you have to capture someone's attention on your website
The researchers discovered that 99% of web pages have a negative aging effect.
Metrics
Bounce rate is a metric that measures the percentage of people who land on your website and do completely nothing on the page they entered. So they don’t click on a menu item, a ‘read more’ link or any other internal links on the page. This means that the Google Analytics server doesn’t receive a trigger from the visitor.
Motives
Posible reasons are:
- The quality of the page is low.
- Your audience doesn’t match the purpose of the page.
- Visitors have not found the information that they were looking for.
UX Factors
- It isn’t Usable. It doesn' work properly on different devices, slow loading, accesibility issues (Hard to Read), broken links
- They don’t know what to do. A common mistake is to give people too much information. Poor Navigation
- You Fail to Impress or Inspire, No matter who your website visitors are, they all have one question: “What’s in it for me?” Your first impression is everything
Think
The thinking stage refers to making assumptions about your product and your users. UX Research gathers information about our target audience, competitors, and the product we want to create. Ideation, is the process of coming up with ideas or hypotheses using design thinking.
Make
Next step is create a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) using several methods, including wireframes 2D, low-fidelity designs of the product, mockups: high-quality more realistic versions and prototype as a simplified versions of the final product, although functionality is limited and not full-scale. Landing pages are a great way to gauge whether there's interest in your product.
Check
Check your MVP with your users and validate or invalidate your hypotheses using user testing methods like A/B testing, usabililty testing sesions, questionaires.
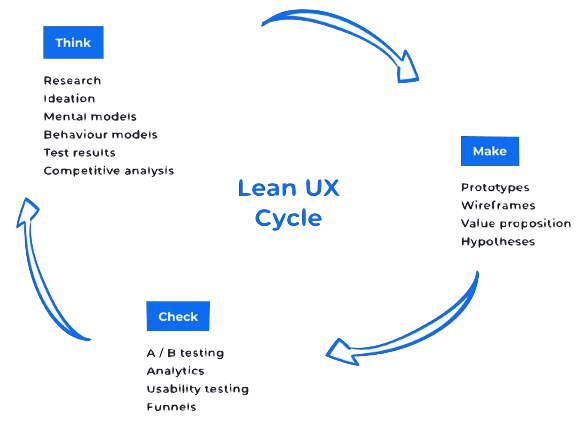
UX Process
Visual Storytelling
- Capture attention: Visually appealing and engaging stories can help to capture users’ attention and keep them interested in the product or service.
- Evoke emotions: Stories that evoke emotions can help users connect with the product or service on a deeper level.
- Communicate complex ideas: Stories can be used to communicate complex ideas in a way that is easy to understand.
- Build brand identity: Stories can help to build brand identity by creating a sense of connection between the user and the product or service.
Features
Visual storytelling is a powerful technique in UI/UX to create immersive and memorable experiences.
By leveraging the principles of storytelling and applying them to the visual elements of a design, designers can evoke emotions, establish a connection with users, and guide them through a meaningful journey trough an story.
The power of visual storytelling lies in its ability to engage users on an emotional level, making the design more relatable and memorable.
Trends on UX Storytelling
This is a page !
- The Definition of User Experience (nngroup), UX Glosary term: User Experience (UX)
- Adam Fard (2022) The Ultimate Guide to Lean UX Design, Medium
- K. Schoenblum (202) Understanding the behemoth that is the UX umbrella, UX Collective
- K. A. Aziz (2023) The Power of Visual Storytelling: Creating Compelling UI Designs, bootcamp design blog
- S. Damiano (2023) The Future of UX/UI: How Emerging Technologies Will Impact Advancements in Digital Design, medium